phaseportbinom2.mws
Plot phase portrait for moment closure equations for Verhulst logistic model, assuming binomial distribution.
This Maple work sheet uses Maple8, and the new package LinearAlgebra. Date 030402.
| > | restart; with(DEtools,DEplot); with(plots,display); with(LinearAlgebra,Eigenvectors); with(VectorCalculus,Jacobian); XP:=Vector(2); |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
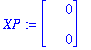
In the original Verhulst model, take alpha1=alpha2=1, R0=4, N=100. Then a1=3/5, f1=5/3, f2=3/5. Take r/K=1 (by rescaling time). Put kappa1=X[1], kappa2=X[2].
The equations are given by the procedure G:
| > | G:=proc(N,t,X,XP) XP[1]:=(60-X[1])*X[1]-X[2]; XP[2]:=(100-0.6*X[1])*X[1]+119.4*X[2]-4*X[1]*X[2]-4*X[2]^2/X[1] +2*X[2]; end; |
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Run G to determine XP:
| > | G(1,t,X,XP): |
Determine the isocline where the first derivative is equal to zero:
| > | isocline1:=solve(XP[1],X[2]); |
![]()
Determine the critical points as the intersection of the two isoclines:
| > | solve(expand(subs(X[2]=isocline1,XP[2])),X[1]); |
![]()
Only the non-zero value of X[1] gives a critical point. (Note that the ODEs are not defined for X[1]=0.)
The critical point is denoted P1.
| > | P1[1]:=%[2]; |
![]()
| > | P1[2]:=subs(X[1]=P1[1],isocline1); |
![]()
Now determine the Jacobian of the right-hand sides of the given system of equations:
| > | J:=Jacobian(XP,[X[1],X[2]]); |
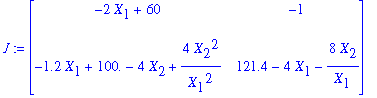
Determine the jacobian at the critical point:
| > | J1:=subs(X[1]=P1[1],X[2]=P1[2],J); |
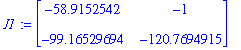
The eigenvalues and eigenvectors of this matrix:
| > | eg1:=Eigenvectors(J1,output=list); |
![eg1 := [[-57.3515746921957117+0.*I, 1, Vector(%id = 20254216)], [-122.333171007804282+0.*I, 1, Vector(%id = 20261444)]]](images/phaseportbinom216.gif)
![eg1 := [[-57.3515746921957117+0.*I, 1, Vector(%id = 20254216)], [-122.333171007804282+0.*I, 1, Vector(%id = 20261444)]]](images/phaseportbinom217.gif)
Notice that P1 is a stable node. Furthermore,
eg1[1]: slow manifold, eg1[2]: fast manifold of stable node P1.
A Maple procedure for determining initial values on each manifold near each critical point follows.
Think of it as transforming eg-to-init (eg2init):
| > | eg2init:=proc(P,eg,d) local u,lu,v,k; u:=eg[3]; # This is an eigenvector. lu:=sqrt(u[1]^2+u[2]^2); # This is the length of the eigenvector u. v:=d*u/lu; # This is a vector of length d in the direction of u. [seq([x(0)=P[1]+(-1)^k*v[1],y(0)=P[2]+(-1)^k*v[2]],k=1..2)]; #These are two initial values near P in the direction of the eigenvector. end proc: |
CHECK the numbering here!
| > | init1fast:=eg2init(P1,eg1[2],10); |
![]()
![]()
Plot two orbits on the fast manifold.
| > | plot1fast:=DEplot(G,[x,y],t=-0.05..0,number=2,init1fast,x=-10..100,y=-100..1000,arrows=none,linecolor=red,stepsize=0.01): plot1fast; |
![[Maple Plot]](images/phaseportbinom220.gif)
Plot one orbit on the slow manifold.
| > | plot1slow:=DEplot(G,[x,y],t=0..0.1,number=2,[[x(0)=500,y(0)=20]],x=-10..100,y=-100..1000,arrows=none,linecolor=red,stepsize=0.001): plot1slow; |
![[Maple Plot]](images/phaseportbinom221.gif)
NOTE: The arrows on the final phase portrait become less pronounced if the commend "color=red" below is replaced by "color=yellow".
| > | plotarrows:=DEplot(G,[x,y],t=0..0.1,number=2,{[x(0)=61,y(0)=31]},x=-10..100,y=-100..1000,linecolor=red,stepsize=0.01,color=red): plotarrows; |
![[Maple Plot]](images/phaseportbinom222.gif)
Plot four additional orbits:
| > | init1:=[x(0)=10,y(0)=0]: plot1:=DEplot(G,[x,y],t=0..0.1,number=2,[init1],x=-10..100,y=-100..1000,stepsize=0.01,arrows=none,linecolor=red): plot1; |
![[Maple Plot]](images/phaseportbinom223.gif)
| > | init2:=[x(0)=10,y(0)=1000]: plot2:=DEplot(G,[x,y],t=0..0.2,number=2,[init2],x=-10..100,y=-100..1000,stepsize=0.002,arrows=none,linecolor=red): plot2; |
![[Maple Plot]](images/phaseportbinom224.gif)
| > | init3:=[x(0)=40,y(0)=1000]: plot3:=DEplot(G,[x,y],t=0..0.1,number=2,[init3],x=-10..100,y=-100..1000,stepsize=0.002,arrows=none,linecolor=red): plot3; |
![[Maple Plot]](images/phaseportbinom225.gif)
| > | init4:=[x(0)=100,y(0)=1000]: plot4:=DEplot(G,[x,y],t=0..0.05,number=2,[init4],x=-10..100,y=-100..1000,stepsize=0.002,arrows=none,linecolor=red): plot4; |
![[Maple Plot]](images/phaseportbinom226.gif)
| > | display({plot1fast,plot1slow,plotarrows,plot1,plot2,plot3,plot4},labels=[Mean,Variance],title=Binomial_Assumption); |
![[Maple Plot]](images/phaseportbinom227.gif)
| > |