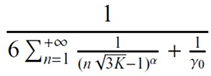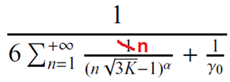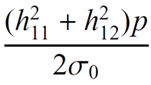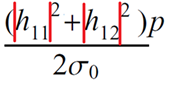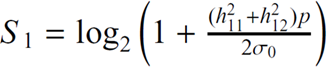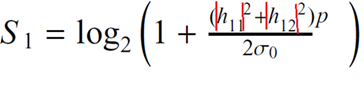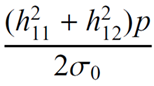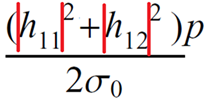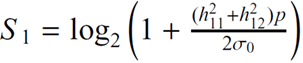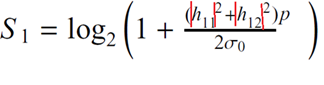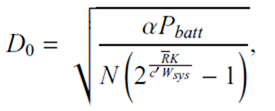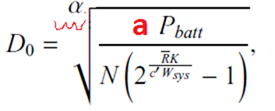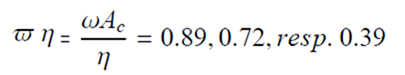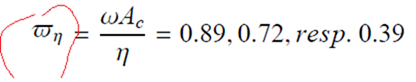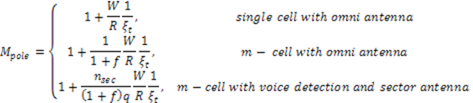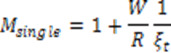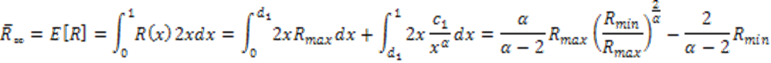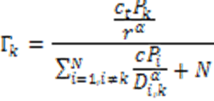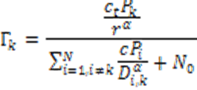| Fundamentals of Mobile Data Networks, |
|
| G. Miao, J. Zander, K. Sung, and B. Slimane |
| Typo/Grammatical Errors |
| S.No |
Chapter
No. |
Chapter
Name |
Page |
Line |
Error |
Correction |
| 1 |
6 |
Transmitter
power control |
152 |
4 |
SIR |
minimum
SIR |
| 2 |
6 |
Transmitter
power control |
154 |
17 |
and
and |
and |
| 3 |
8 |
Association
and handover |
214 |
last |
candidate |
neighbor |
| 4 |
5 |
Principles
of cellular systems |
105 |
9 |
|
|
| 5 |
10 |
Long
term evolution |
265 |
9
from the bottom |
|
|
| 6 |
10 |
Long
term evolution |
265 |
8
from the bottom |
|
|
| 7 |
10 |
Long
term evolution |
266 |
11 |
|
|
| 8 |
10 |
Long
term evolution |
266 |
12 |
|
|
| 9 |
3 |
Medium
access control |
56 |
last
line, eq (3.43) |
|
|
| 10 |
3 |
Medium
access control |
48 |
Figure
3.17 |
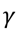
|
|
| 11 |
3 |
Medium
access control |
53 |
Figure
3.20 |
Label
of teminalL: A, B, C, D |
Should
be: B, A, C, D. |
| 12 |
5 |
Principles
of cellular systems |
131 |
3 |
As
L approaches the system °≠ |
As
L approaches 1, the system °≠ |
| 13 |
5 |
Principles
of cellular systems |
125 |
Figure
5.17: 4th subplot |
Set
o forthorognal codes |
Set
of orthorognal codes |
| 14 |
9 |
Energy-efficient
design |
237 |
Formula
9.26, 9.27, Fig. 9.5. Last
paragraph of page 237. ln2 conefficient is missing in all the formulas, as
shown in the right two columns. |
|
|
| 15 |
10 |
Long
term evolution |
259 |
5 |
As
shown in Figure 3.6 |
As
shown in Figure 3.7 |
| 16 |
11 |
Wireless
infrastructure economics |
293 |
Equation
(11.20) |
|
|
| 17 |
8 |
Association
and handover |
210 |
Figure
8.7, fourth formula in the bottom |
(N_tot+1)¶Ő |
(N_thr+1)¶Ő |
| 18 |
10 |
Long
term evolution |
268 |
Figure
10.8, second line, second block: S/P |
"Parallel
to Serial". |
Serial
to Parallel |
| 19 |
Ch
8 |
Association
and handover |
212 |
Figure
8.9 |
Two
'N_thr' in the circles |
'N_tot' |
| 20 |
Ch
9 |
Energy-efficient
design |
240 |
Line
3 |
It
consumes P_1 circuit power in transmission mode and P_2 circuit power °≠. |
It
consumes P_2 circuit power in transmission mode and P_1 circuit power °≠. |
| 21 |
Ch
9 |
Energy-efficient
design |
235 |
Line
12, the equation in (3) |
|
|
| 22 |
Ch
5 |
Principles
of cellular systems |
108 |
Line
4, left side of the equation |
|
|
| 23 |
Ch
5 |
Principles
of cellular systems |
117 |
Figure
5.13, Y axis. Read the three lables. They should be of the same format |
100 |
10^0 |
| 24 |
Ch
7 |
Interference
Management |
191 |
line
5 |
|
|
| 25 |
Ch
8 |
Association
and handover |
205 |
line
3 |
k
dB samples |
k
samples |
| 26 |
Ch
3 |
Medium
access control |
55 |
equation
3.38 |
Pr(At
least one arrival in the first k-1 slots) |
Pr(At
least one arrival in each of the first k-1 slots) |
| 27 |
Ch
6 |
Transmitter
power control |
172 |
Line 10 |
S*P_t |
S
°Ń P_t |
| 28 |
Ch
11 |
Wireless
infrastructure economics |
287 |
Equation
11.8 |
in
f ra |
infra |
| 29 |
Ch
11 |
Wireless
infrastructure economics |
289 |
Figure
11.3 |
the
curve in the middle has no legend |
add
legend "Cost" next to the black solid line |
| 30 |
Ch
11 |
Wireless
infrastructure economics |
291 |
17 |
in
f ra |
infra |
| 31 |
Ch
0 |
Acronyms |
xiv |
13 |
Space
Frequecy Block Code |
Space
Frequency Block Code |
| 32 |
Ch
0 |
Acronyms |
xv |
last
line |
¶« Normalized thermal noise |
¶« Normalized thermal noise ( sometimes
used as number of channel/cell ) |
| 33 |
Ch
9 |
Energy-efficient
design |
230 |
Eq.
9.7 |
E
= pt |
E=Pt |
| 34 |
Ch
10 |
Long
term evolution |
269 |
last |
12
REs |
84
REs |
| 35 |
5 |
Principles
of cellular systems |
132 |
15 |
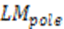
|
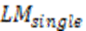
|
| 36 |
5 |
Principles
of cellular systems |
132 |
Formula
5.67 |
|
|
| 37 |
5 |
Principles
of cellular systems |
132 |
Formula
5.70, replace completely. |
|
|
| 38 |
5 |
Principles
of cellular systems |
138 |
line
22, Problem 5.7 |
"Determine
the minimum distance between°≠" |
"Determine
the maximum distance between°≠" |
| 39 |
5 |
Principles
of cellular systems |
139 |
Line
14, Problem 5.10 |
|
|
| 40 |
5 |
Principles
of cellular systems |
139 |
Line
5 from bottom, Problem 5.11 |
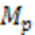
| "Determine the pole capacity
of this system°≠" |
|
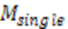
| "Determine the single-cell capacity
of this system°≠" |
|
| 41 |
5 |
Principles
of cellular systems |
112 |
Equation
below figure 5.12 |
missing
equation number |
Add
equation number (5.21) |
| 42 |
5 |
Principles
of cellular systems |
114 |
Equation 5.21 |
wrong
equation number |
remove
equation number (5.21) |
| 43 |
5 |
Principles
of cellular systems |
113 |
Line
5 from bottom |
This
a quite common situation |
"This
is a quite common situation" |
| 44 |
5 |
Principles
of cellular systems |
114 |
Equation
5.21, replace completedly. |
|
| 45 |
3 |
Medium
access control |
53 |
Figure
3.19 |
Label
of teminalL: A, B, A |
Should
be: A, C, B. |
| 46 |
5 |
Principles
of cellular systems |
119 |
Table
5.2 |
29 |
19 |
| 47 |
5 |
Principles
of cellular systems |
128 |
Line
3 |
where
G_{k,l} is the link gain between mobile terminal l and base station k |
where G_{l,k} is the link gain between
mobile terminal k and base station l |
| 48 |
2 |
Wireless
Network Models |
14 |
11 |
doppler
shift |
Doppler
shift |
| 49 |
4 |
Scheduling |
72 |
22 |
cancelation
(SIC) |
cancellation
(SIC) |
| 49 |
4 |
Scheduling |
72 |
4th
from the bottom |
the
cancelation order |
the
cancellation order |
| 50 |
5 |
Principles
of Cellular Systems |
96 |
10 |
and
the path loss constant. |
and
¶Ń the path loss constant. |
| 51 |
5 |
Principles
of Cellular Systems |
98 |
10 |
the
received SIR reduces to |
the
received SINR reduces to |
| 52 |
8 |
Mobility
and Handover |
206 |
14 |
much.The
drawback of such |
much.
The drawback of such |
| 53 |
1 |
Introduction |
10 |
second last line |
Chapter
11 |
Chapter
10 |
| 54 |
2 |
Wireless
network models |
24 |
Figure
2.7 |
G
and G' |
G
and G' should be in bold as G
and G' |
| 55 |
2 |
Wireless
network models |
25 |
Line
22, Excercise 2.1 |
Section
2.1 |
Example
2.1 |
| 56 |
3 |
Medium
access control |
39 |
Line
4 from bottom, in between formula 3.15 and 3.16 |
and
the system throughput is |
with
N_m as the number of symbols per message, and the system throughput is |
| 57 |
4 |
Scheduling |
76 |
Line
17, formula 4.6 |
i[t+1]=i[t]+1 |
i[t+1]=mod(i[t]+1,
N), with N as the number of users |
| 58 |
5 |
Principles
of cellular systems |
99 |
Formula
in the bottom, 3rd line from bottom |
|
|
| 59 |
8 |
Association
and handover |
203 |
Figure
8.2, Y-axis |
Signal
quantity |
Signal
quality |
| 60 |
8 |
Association
and handover |
210 |
Figure
8.7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|